
| Tweet |

Custom Search
|
|

|
||
 TM 55-1905-223-24-5
(3)
Visually inspect the bearings (11) for damage.
NOTE
Replace any bearings with lock tang damage or scratches
(deep enough to be felt with a fingernail). Also replace any
bearings which show pitting, flaking, or corrosion in the
copper lining.
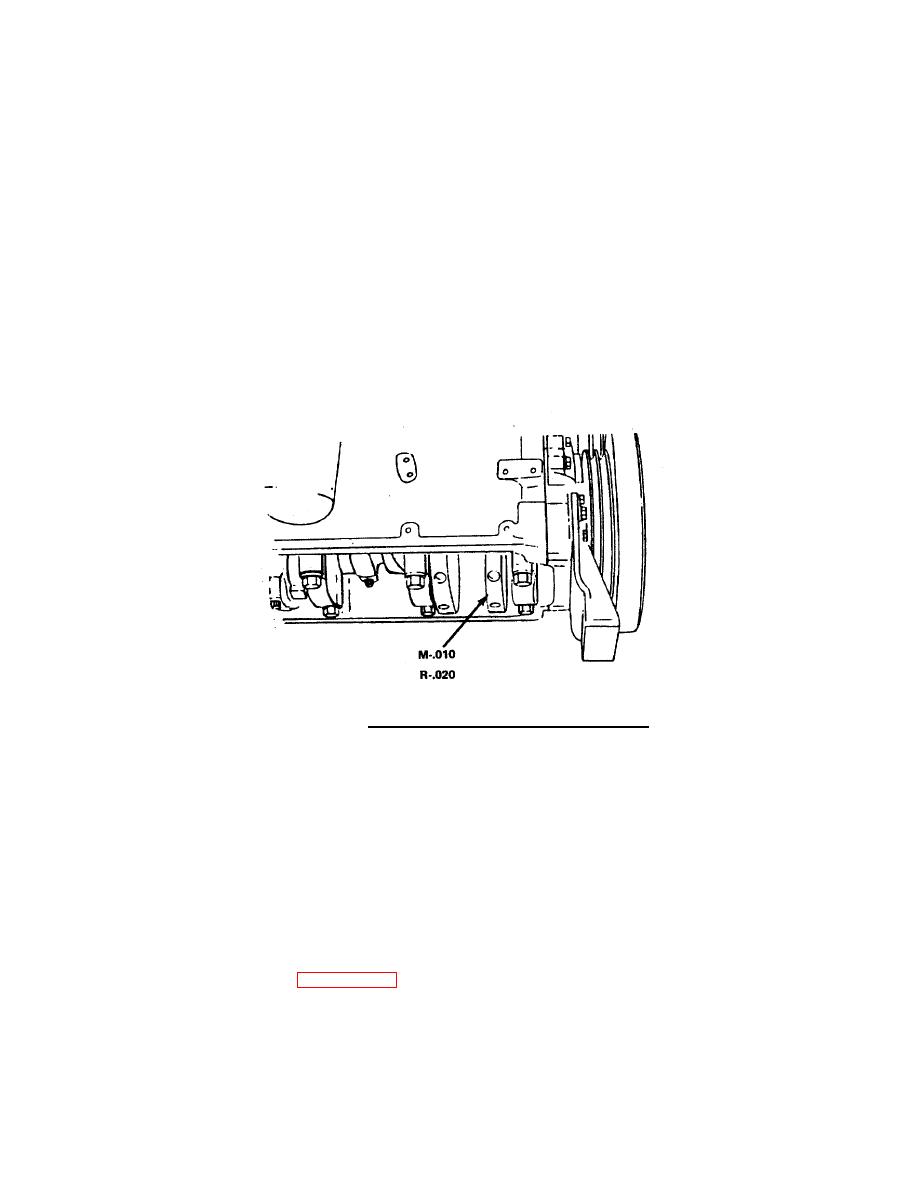
Bearing shells (12) are available for crankshafts which are
0.010 inch (0.25 mm), 0.020 inch (0.51 mm), 0.030 inch
(0.76 mm), or 0.040 inch (1.02 mm) undersize. Crankshafts
which are ground undersize in the connecting rod or the
main bearing journals are marked on the front counter
weight. If the crankshaft is marked, check the bearing shell
to make sure the correct bearing size is used (FIGURE 4-
33) .
FIGURE 4-33. Counterweight Markings for Bearing Sizes.
NOTE
Normal bearing wear produces a smooth finish which will wear
into the copper lining. Exposed copper does not always indicate
worn bearings. If large areas of copper lining are visible in the
bearings before the engine has accumulated 3,750 hours,
inspect the engine for contamination from fine dirt particles and
correct the problem.
(4)
Visually inspect the bearing seating surface for nicks or burrs.
(5)
If nicks or burrs cannot be removed with a fine crocus cloth, the
bearings (11, FIGURE 4-31) must be replaced.
(6)
Measure the rod bearing shell (11) thickness with an outside micrometer
that has a ball tip.
4-68
|
||
 |
||